Prioritized Experience Replay 介绍了优先经验回放机制,本文将该机制与 Double DQN 进行简单的结合,同时还要介绍在前文中提到的 Sum Tree 数据结构,它能高效的在记忆库中进行基于优先经验回放机制的抽样。直接看代码
Sum Tree
由于使用贪婪法来选取优先经验的时间复杂度太高,同时还有其他问题,所以我们用 \(P(i) =p_i^\alpha / \sum_kp_k^\alpha\) 来定义某个片段的选取概率,其中 \(p_i\) 我们将它等同于 TD-error \(|\delta_i|\) ,并用 Sum Tree 这种数据结构来表示每个存储的片段。
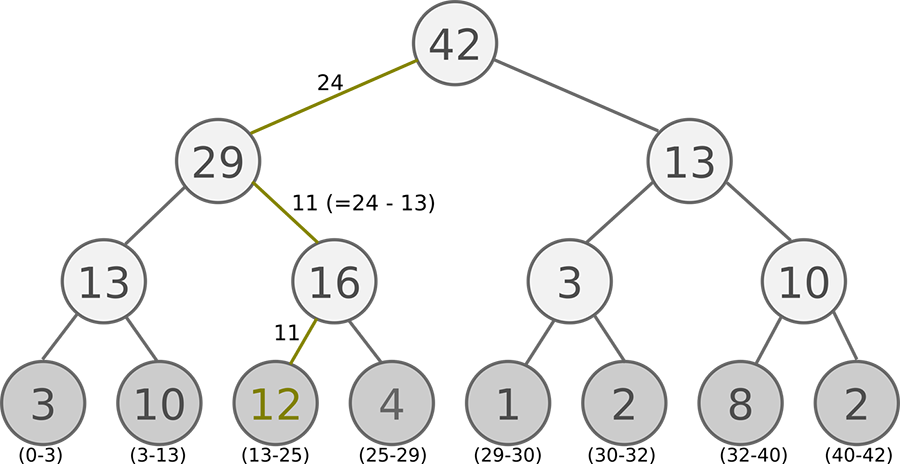
Sum Tree 是一种二叉树类型的数据结构,所有叶子节点存储优先级 \(p_i\) ,所有父节点为子节点之和,所以这棵树的根节点即为所有叶子节点的和,如下图所示:
在抽样时,我们将存储的优先级的个数除以 batch size ,分成 batch size 个区间,如图中的例子,一共有 3, 10, 12, 4, 1, 2, 8, 2 八个优先级节点,如果 batch size = 6 ,那么分成: [0-7], [7-14], [14-21], [21-28], [28-35], [35-42] 六个区间,再分别在六个区间中均匀地随机选择一个数,从根节点依次往下搜索。如在第 4 个区间中选中了 24 ,则将 24 与根节点的左节点进行比较,因为 24 < 29 所以继续往左搜索,将 24 与 29 的左节点比较,发现 24 > 13 ,则继续往右搜索,同时将 24 - 13 = 11 ,将 11 与 16 的左节点比较,11 < 12 ,因为 12 已经是叶子节点,则搜索完毕,选中 12 这个优先级。
图中叶子节点下面括号中的区间代表该优先级可以被搜索到的范围,由此可见优先级大的被搜索到的概率越高,同时优先级小的,也有一定概率被选中。
我们用顺序存储来实现这个二叉树,为了方便,我们规定 sum tree 必须是满二叉树:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 class SumTree : def __init__ (self, capacity) : self.capacity = capacity self.tree = [0 ] * (2 * capacity - 1 ) self.data = [None ] * capacity self.size = 0 self.curr_point = 0 def add (self, data) : self.data[self.curr_point] = data self.update(self.curr_point, max(self.tree[self.capacity - 1 :self.capacity + self.size]) + 1 ) self.curr_point += 1 if self.curr_point >= self.capacity: self.curr_point = 0 if self.size < self.capacity: self.size += 1 def update (self, point, weight) : idx = point + self.capacity - 1 change = weight - self.tree[idx] self.tree[idx] = weight parent = (idx - 1 ) // 2 while parent >= 0 : self.tree[parent] += change parent = (parent - 1 ) // 2 def get_total (self) : return self.tree[0 ] def get_min (self) : return min(self.tree[self.capacity - 1 :self.capacity + self.size - 1 ]) def sample (self, v) : idx = 0 while idx < self.capacity - 1 : l_idx = idx * 2 + 1 r_idx = l_idx + 1 if self.tree[l_idx] >= v: idx = l_idx else : idx = r_idx v = v - self.tree[l_idx] point = idx - (self.capacity - 1 ) return point, self.data[point], self.tree[idx] / self.get_total()
Memory
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Memory (object) : def __init__ (self, batch_size, max_size, beta) : self.batch_size = batch_size self.max_size = 2 **math.floor(math.log2(max_size)) self.beta = beta self._sum_tree = SumTree(max_size) def store_transition (self, s, a, r, s_, done) : self._sum_tree.add((s, a, r, s_, done)) def get_mini_batches (self) : n_sample = self.batch_size if self._sum_tree.size >= self.batch_size else self._sum_tree.size total = self._sum_tree.get_total() step = total // n_sample points_transitions_probs = [] for i in range(n_sample): v = np.random.uniform(i * step, (i + 1 ) * step - 1 ) t = self._sum_tree.sample(v) points_transitions_probs.append(t) points, transitions, probs = zip(*points_transitions_probs) max_impmortance_ratio = (n_sample * self._sum_tree.get_min())**-self.beta importance_ratio = [(n_sample * probs[i])**-self.beta / max_impmortance_ratio for i in range(len(probs))] return points, tuple(np.array(e) for e in zip(*transitions)), importance_ratio def update (self, points, td_error) : for i in range(len(points)): self._sum_tree.update(points[i], td_error[i])
参考
Schaul, T., Quan, J., Antonoglou, I., & Silver, D. (2015). Prioritized experience replay. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.05952 .
https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/reinforcement-learning/4-6-prioritized-replay/
感谢 王健树 StepNeverStop 帮助我理解了 Sum Tree 🙏🙏🙏