在 DeepMind 的 Asynchronous Methods for Deep Reinforcement Learning 一文中,介绍了另一种简单的轻量级深度强化学习框架——异步地进行深度神经网络梯度下降。该框架可以适用于许多强化学习算法,论文中将框架套在了四种标准强化学习算法上,分别是 one-step Q-Learning, one-step Sarsa, n-step Q-Learning 和 Advantage Actor-Critic ,都取得了不错的稳定效果。其中最后一个 Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic (A3C) 算法更是有着最好的性能表现,在多核 CPU 上学习比在 GPU 上学习的时间减少了一半,本文也会重点关注 A3C 算法。
Asynchronous one-step Q-Learning
Q-Learning 已经很熟悉,用参数 \(\theta\) 来表示近似的行为价值函数 \(Q(s,a; \theta)\) ,则近似函数通过最小化以下代价函数来进行学习: \[ L_i(\theta_i) = \mathbb{E}\left( r+\gamma\max_{a'} Q(s',a';\theta_{i-1}) - Q(s,a;\theta_i) \right)^2 \] 以上的 Q-Learning 称为 one-step Q-learning ,因为目标值为 $ r+_{a’} Q(s’,a’;) $ ,只向前走了一步,便进行更新。套用异步强化学习框架后的算法为:
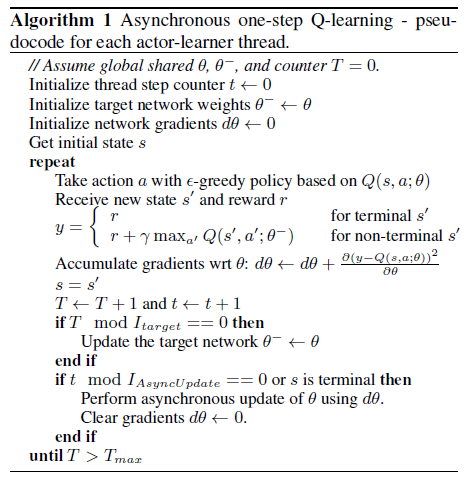
算法的大致流程是:有两个全局的 \(Q(s,a; \theta)\) 和 \(Q(s,a; \theta^-)\) 神经网络,每个线程并行地、独立地以 ϵ-greedy 方式进行行为的探索,然后根据 Q-Learning 算法更新 \(\theta\) 参数,但这里的更新不是直接将更新提交到全局 \(Q(s,a; \theta)\) 网络中,而是先自己保留更新的梯度,再每隔一段时间,将自己的梯度更新到全局神经网络中,同时每隔一段时间将全局神经网络参数同步到自己的参数中。
Asynchronous one-step Sarsa
asynchronous one-step sarsa 算法与 asynchronous one-step Q-learning 算法基本相同,区别只在于 sarsa 是同策略的 Q-learning ,所以目标值换为 \(r+\gamma Q(s',a';\theta^-)\) 。
Asynchronous n-step Q-Learning
在 one-step Q-learning 的基础上,如果是先向前走 n 步再进行更新,则称为 n-step Q-learning,目标函数为 \(r_t+\gamma r_{t+1} + \cdots + \gamma^{n-1} r_{t+n-1} + \gamma^n \max_aQ(s_{t+n},a;\theta)\) ,这比 one-step Q-learning 会更有效一点。
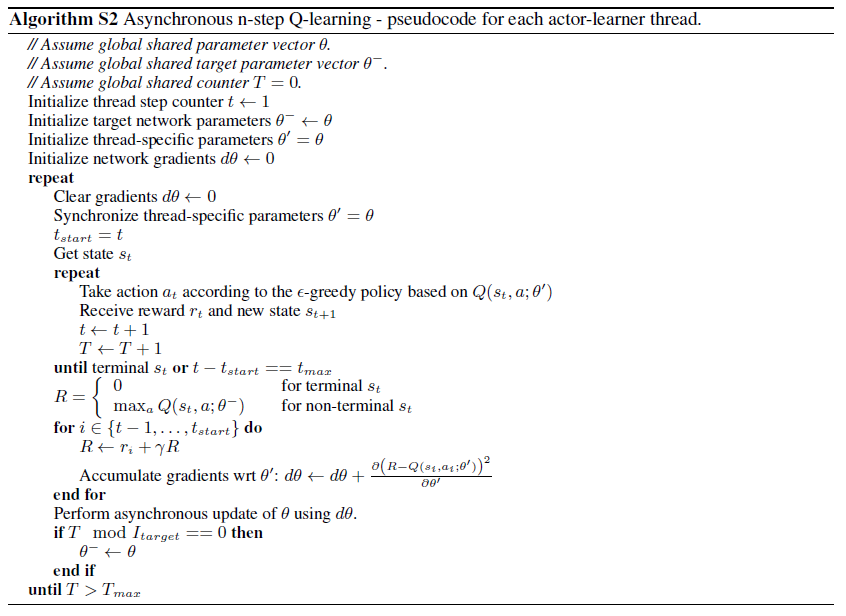
常见的情况下,一般会用后向视角 (backward view) 即用资格迹 (eligibility traces) 来更新,但这个算法用了不大常见的正向视角 (forward view) ,作者解释因为在以动量梯度更新的方式训练神经网络和反向传播过程中,正向视角更加简单。
Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic
A3C 算法也是根据传统的策略梯度算法修改而来,套上了异步的框架,估计 \(\pi(a_t|s_t;\theta)\) 与价值函数 \(V(s_t;\theta_v)\) 。类似于 n-step Q-learning 的变体形式, A3C 算法也是采用前向视角,用向前走的 n 步奖励来进行学习。根据在策略梯度中提到的基准函数与 Advantage Function \(A(s_t,a_t;\theta,\theta_v)\),在 A3C 中同样也用 TD-error 来无偏地代替 Advantage Function :\(\sum_{i=0}^{k-1} \gamma^i r_{t+i} + \gamma^k V(s_{t+k};\theta_v) - V(s_t;\theta_v)\) 。具体算法为:
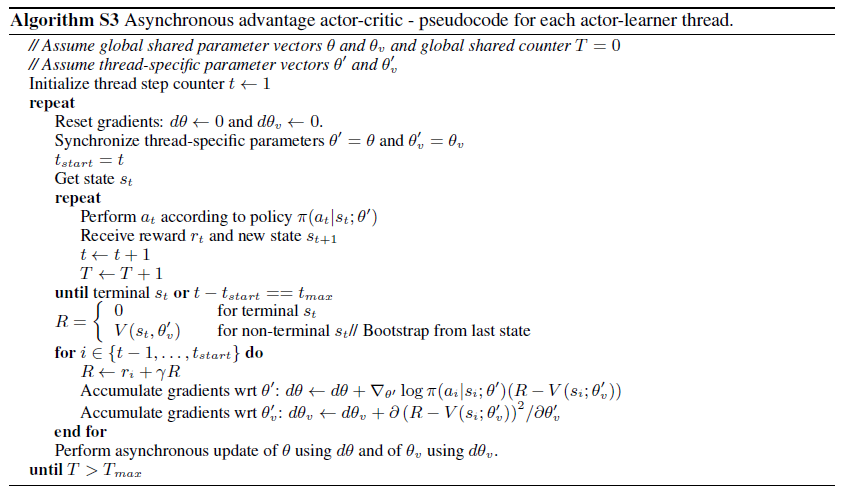
大致流程为:全局有策略、价值函数两个神经网络,同时每个线程也有自己独立的一套套策略、价值函数神经网络,在初始化时,线程中的神经网络参数与全局的相同。每个线程独立地进行行为的探索,然后更新到自己的神经网络中,并且保留梯度数据。每隔一段时间,子线程将梯度更新到全局参数中,并且将全局的参数拉取下来替换自己的神经网络参数。
参考
Mnih, V., Badia, A. P., Mirza, M., Graves, A., Lillicrap, T., Harley, T., … & Kavukcuoglu, K. (2016, June). Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning. In International Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 1928-1937).
https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/reinforcement-learning/6-3-A1-A3C/

